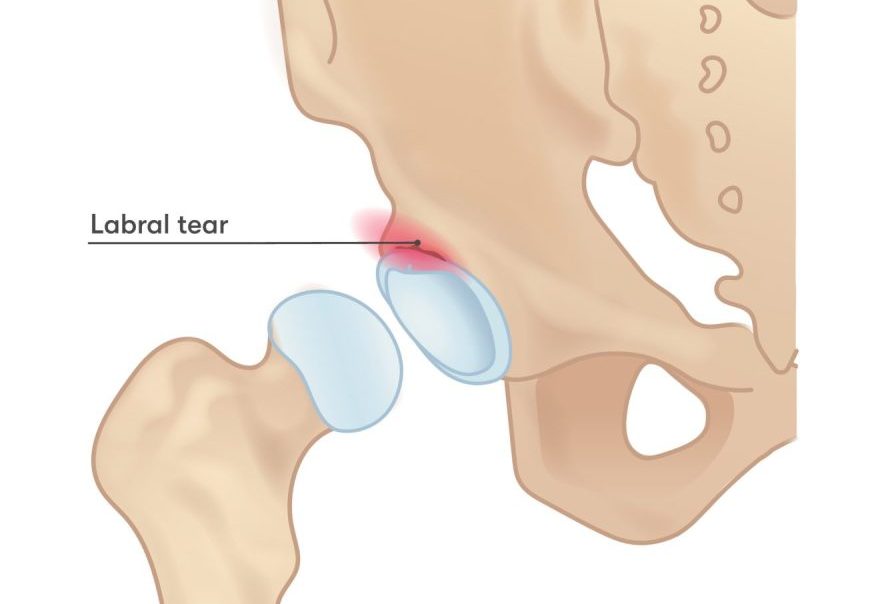
Hip labral tears are a common injury that affects the labrum, a ring of cartilage that surrounds the hip joint socket. The labrum provides stability, cushioning, and support to the hip joint. A tear in the labrum can result from trauma, repetitive motions, structural abnormalities, or degenerative conditions.
Symptoms of a hip labral tear may include groin pain, clicking or catching sensations in the hip joint, stiffness, limited range of motion, and instability. The pain may worsen with activities that involve hip flexion, rotation, or prolonged sitting. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are important to manage symptoms, prevent further damage, and restore hip function. Treatment for a hip labral tear typically involves a combination of physiotherapy and pain management, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
Applying the 5 stages of rehab to a hip labral tear can help optimize recovery and improve hip function.
Pain and symptom management. The first stage of rehab focuses on pain reduction and inflammation control. This may involve rest, ice, and pain-relieving medications prescribed by a healthcare professional. Physiotherapy treatments such as muscle activation exercises, soft tissue massage, and gentle range of motion exercises can also help to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Range of motion. Once pain is managed, the focus shifts to restoring normal range of motion in the hip joint. Physiotherapy exercises and stretches are prescribed to improve hip flexibility and increase the range of motion. This may include gentle hip movements in different planes, such as flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation,with gradual progression as tolerated.
Motor control. In stage 3, the emphasis is on improving neuromuscular control and stability around the hip joint. Exercises that target the muscles surrounding the hip, including the deep hip stabilizers, glutes, hip abductors, and hip external rotators, are incorporated to improve muscle strength, balance, and coordination. Core stability exercises may also be included to provide additional support to the hip joint.
Strengthening. Stage 4 focuses on strengthening the muscles around the hip joint to improve stability and support the joint. This typically involves targeted resistance training exercises such as squats, lunges, bridges, and clamshells. Strengthening exercises should be performed with proper form and under the guidance of a physiotherapist to ensure optimal muscle activation and to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
Maintenance. The final stage of rehab involves maintaining the gains achieved in the previous stages and preventing future hip joint issues. This may involve continuing with a tailored exercise program that includes strengthening exercises, range of motion exercises, and functional activities. It is important to be aware of hip mechanics during daily activities and sports participation to minimize the risk of future injury.
Throughout the rehab process, close collaboration with a physiotherapist and/or other healthcare professionals is essential. They will guide the rehabilitation program, monitor progress, and make necessary adjustments to ensure the best outcomes. With proper management and rehabilitation, individuals with a hip labral tear can experience reduced pain, improved hip function, and a return to their desired level of activity.
For more information regarding hip labral tears please visit:
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Hip_Labral_Disorders
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2697339/